Finding the slope on a table may seem daunting at first, but with a straightforward approach, you can master this essential skill effortlessly. To find the slope on a table, simply identify two points on the table, calculate the change in the y-values over the change in the x-values, and voilà, you have your slope. Understanding how to find the slope on a table can unlock a deeper comprehension of relationships and patterns in data. Let’s delve into the step-by-step process and demystify the concept of slope calculation on a table.
Discovering the Secrets of Finding the Slope on a Table
Welcome, young mathematicians! Today, we are going to embark on an exciting journey to uncover the mysteries of finding the slope on a table. Whether you are a budding math enthusiast or someone looking to brush up on their skills, this guide will help you navigate the world of slopes with confidence. So, fasten your seatbelts, grab your pencils, and let’s dive into the fascinating realm of slope calculations!
What is a Slope?
Before we delve into the nitty-gritty of finding the slope on a table, let’s first understand what exactly a slope is. In math, the slope represents the steepness of a line. It tells us how much a line rises or falls as we move along it. Imagine walking up a hill – the slope of the hill indicates how steep or gentle the climb is.
Understanding the Basics of Slope Calculation
Now, let’s talk about how we can calculate the slope of a line using a table of values. The slope is determined by looking at how the y-values change concerning the x-values. In simpler terms, it’s about how much the line goes up or down compared to how much it goes right. Sounds tricky? Don’t worry; we’ll break it down step by step!
Gather Your Data
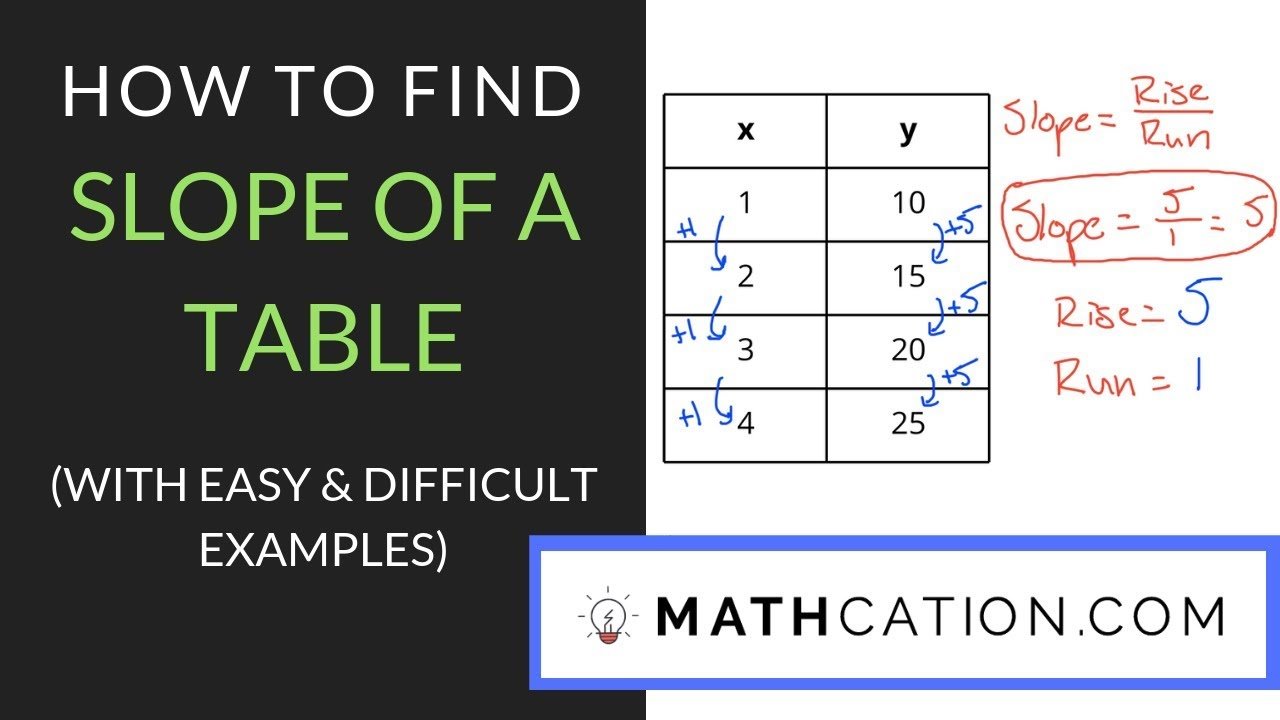
The first step in finding the slope on a table is to gather your data. Look at the table provided and identify the x and y values. These values represent points on the line. For example, let’s say our table looks like this:
| x | y |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 3 | 7 |
In this table, the x-values are 1, 2, and 3, while the corresponding y-values are 3, 5, and 7. Now that we have our data, let’s move on to the next step.
Calculate the Rise and Run
To find the slope, we need to calculate the rise and the run. The rise is the difference between two y-values, while the run is the difference between the corresponding x-values. The formula for slope is:
Slope = (Change in y) / (Change in x)
Let’s use our table to calculate the slope. First, we need to choose two points. Let’s say we pick the points (1, 3) and (2, 5). The rise is 5 – 3 = 2, and the run is 2 – 1 = 1. Therefore, the slope is:
Slope = 2 / 1 = 2
Congratulations! You’ve successfully found the slope of the line using two points from the table. But wait, there’s more to explore!
Using Multiple Points to Find the Slope
While calculating the slope with two points is a great start, sometimes using more points can give us a better understanding of the line’s steepness. By comparing multiple sets of points, we can ensure the accuracy of our slope calculation.
Calculating Slope with Three Points
Now, let’s take our table with three points: (1, 3), (2, 5), and (3, 7). To calculate the slope, we can choose any two points. Let’s use the points (1, 3) and (3, 7). The rise is 7 – 3 = 4, and the run is 3 – 1 = 2. Thus, the slope is:
Slope = 4 / 2 = 2
Amazing! The slope we calculated matches the slope we found using just two points. It’s like having a backup to confirm our findings. Remember, practice makes perfect, so feel free to try with different sets of points to master the art of finding the slope on a table!
Applying Your Knowledge
Now that you’ve learned how to find the slope on a table using different sets of points, it’s time to put your skills to the test. Look around you – can you spot any inclined surfaces? Try to estimate the slope of a ramp or stairs by observing how much it rises over a given distance. Who knew slope calculations could be so fun and practical?
Congratulations, young mathematicians! You’ve completed your crash course on finding the slope on a table. Remember, slopes are all around us, whether we’re exploring the great outdoors or drawing graphs in math class. By mastering the art of slope calculations, you’ve taken a significant step towards becoming a math whiz! Keep practicing, keep exploring, and most importantly, keep having fun with math!
Until next time, happy calculating!
How to find Slope of a Table | Mathcation
Frequently Asked Questions
What tools do I need to find the slope on a table?
To find the slope on a table, you will need a ruler or a measuring tape to measure the vertical distance and a ruler to measure the horizontal distance. You will also need a calculator to perform the division required to calculate the slope.
How can I calculate the slope on a table?
To calculate the slope on a table, choose two points on a straight line in the table. Measure the vertical distance between the two points and the horizontal distance. Divide the vertical distance by the horizontal distance to find the slope. The slope is the ratio of the change in the y-coordinate to the change in the x-coordinate.
Can the slope on a table be negative?
Yes, the slope on a table can be negative. A negative slope indicates that the line on the table is decreasing from left to right. This means that as the x-coordinate increases, the y-coordinate decreases. Positive slopes indicate an increasing trend.
What does the slope on a table represent?
The slope on a table represents the rate at which the dependent variable changes concerning the independent variable. In simpler terms, it shows how much the y-value changes for every unit increase in the x-value. A steep slope indicates a rapid change, while a gentle slope represents a slow change.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, finding the slope on a table is essential in various fields. By selecting two points on the table and calculating the ratio of the vertical change to the horizontal change, you can determine the slope accurately. Remember, the slope represents the rate of change between two variables. Practice identifying points and applying the slope formula for a better understanding. Mastering how to find the slope on a table empowers you to interpret and analyze data effectively.
